HPC@RUB
Welcome to High Performance Computing (HPC) at Ruhr-Universität Bochum!
Get an overview of HPC resources, apply for access to these HPC resources, and learn how to use them.
In case of problems, have a look at the FAQ section and get help.
Welcome to High Performance Computing (HPC) at Ruhr-Universität Bochum!
Get an overview of HPC resources, apply for access to these HPC resources, and learn how to use them.
In case of problems, have a look at the FAQ section and get help.
HPC@RUB News - also available via RSS Feed or the hpc-news mailing list.
IT.SERVICES offers Linux and HPC introductory training courses for the Universitätsallianz Ruhr. Please register for the Moodle courses. If you’re unsure whether you need the course, you can take the quiz provided in the Moodle course to assess your knowledge of Linux or HPC.
If you find that you don’t need the course or can’t attend, please deregister to allow others to take one of the limited spots.
Introduction to Linux:
Introduction to HPC:
The Open Consultation Hour will not take place due to all members of the HPC@RUB team being unavailable on the following dates:
If you need assistance please write an email to hpc-helpdesk@ruhr-uni-bochum.de in order to open a ticket.
Your HPC@RUB Team
As an early Christmas present to all our users we increased the /home quota to 100G, the /lustre quota to 4.5T, and the /lustre file limit to 1.9M.
We wish you a joyful holiday season and a productive December.
Your HPC@RUB Team
Starting in October, we offer an open consultation hour every Wednesday at 14:00 via Zoom.
The consultation hour is open to all RUB members - please log in before joining the Zoom meeting.
Zoom link: https://ruhr-uni-bochum.zoom-x.de/j/68445033482?pwd=9o95EZacuJBIQ2F7Nb6ju8U7x4GYjm.1
IT.SERVICES offers Linux and HPC introductory training courses as part of the Universitätsallianz Ruhr. Please register for the Moodle courses. If you’re unsure whether you need the course, you can take the quiz provided in the Moodle course to assess your knowledge of Linux or HPC.
If you find that you don’t need the course or can’t attend, please deregister to allow others to take one of the limited spots.
Introduction to Linux:
Introduction to HPC:
We are happy to announce that job monitoring via ClusterCockpit is now available at jobmon.hpc.rub.de!
ClusterCockpit is a new web-based system for job-specific performance and energy monitoring for HPC clusters. It is developed under the MIT open source license at the NHR center NHR@FAU, with contributions from several other HPC centers, including HPC@RUB. Development is funded by the BMBF as part of the Energy-Efficient HPC project.
HPC@RUB is the fourth HPC center to provide ClusterCockpit, and the first Tier-3 center.
Documentation is available at rub.de/hpc/documentation/jobmonitoring.
An online tutorial will be held at March 31, 10:00 via Zoom
We created the HPC User room in the RUB Matrix Server. Please join! This room is for exchange and collaboration between HPC users at RUB.
The HPC team is also present, but please note that you should still contact us at hpc-helpdesk@ruhr-uni-bochum.de if you need a problem solved.
The launch event for the Elysium cluster took place yesterday, see the IT.SERVICES News.
We are happy to announce that the Elysium cluster started operations and is now open for all researchers at RUB!
IT.SERVICES is offering the course “Introduction to High Performance Computing” again.
It will take place on December 11th 2024 in IA 0/65 in a hybrid format. There will be a lecture with interactive exercises on an HPC system. For the exercises we will provide 15 accounts. The accounts will be given to the first 15 in-person participants. Note that we can not give any accounts to remote participants. Please register in the Moodle course to participate. If you are unsure whether you need the course, you can take the quiz provided in the Moodle course to assess your knowledge of HPC.
For successful participation in the course, solid basic knowledge of Linux systems, especially the BASH shell, is required. We also offer courses for this (Introduction to Linux: November 27th, 9:00-12:30, Registration Linux).
Introduction to HPC:
IT.SERVICES is offering two introductions to the Tier-3 HPC system via Zoom, providing an overview of the system and access possibilities.
Topics:
Dates:
If you are interested, please contact us to get the Zoom link.
If you are unable to attend the offered dates, please let us know so that we can offer an alternative date.
IT.SERVICES is offering two training courses with limited participant numbers. Please register for the Moodle courses. If you’re unsure whether you need the course, you can take the quiz provided in the Moodle course to assess your knowledge of Linux or HPC.
If you find that you don’t need the course or can’t attend, please deregister to allow others to take one of the limited spots.
Introduction to Linux:
Introduction to HPC:
The HPC Cluster Elysium is the central HPC facility of Ruhr-Universität Bochum. Its main governing structure is the HPC Advisory Board.
Other options include HPC centres in NRW and elsewhere.
The HPC@RUB cluster Elysium is operated by the HPC team at IT.SERVICES.
The governing structure of HPC@RUB is defined in the Terms of Use.
The HPC Advisory Board consists of five elected RUB scientists and two IT.SERVICES employees.
The five members of the current HPC Advisory Board, elected on April 18 2024, are:
One of the main tasks of the HPC Advisory Board is to allocate a so-called FairShare of the HPC resources to Faculties, Research Centres, and Research Departments. Part of the FairShare is always reserved for scientists whose facility does not have its own allocated FairShare, so that the HPC resources are open to every scientist at RUB.
The FairShare is a percentage that determines how much of the resources is available to a given facility on average. A facility with a 10% FairShare can use 10% of the cluster 24/7 on average. If it uses less, others can make use of the free resources, and the priority of the facility to get the next job to run on the cluster will grow. If it uses more (because others don’t make full use of their FairShare), its priority will shrink accordingly. FairShare usage tracking decays over time, so that it is not possible to save up FairShare for nine months and then occupy the full cluster for a full month.
Within a given facility, all scientists that are HPC project managers share its FairShare. All HPC projects share the FairShare of their manager. Finally, all HPC users share the FairShare of their assigned project. This results in the FairShare tree that has become the standard way of managing HPC resources.
HPC resources are managed based on projects to which individual users are assigned. The purpose of the projects is to keep an account of resource usage based on the FairShare of project managers within the FairShare of their facility.
Professors and group leaders can apply to become project managers; see the Terms of Use for details.
A project manager may apply for projects, and is responsible for compliance with all rules and regulations. Projects will be granted after a basic plausibility check; there is no review process, and access to resources is granted solely based on the FairShare principle, not based on competing project applications.
Users need to apply for access to the system, but access is only active if the user is currently assigned to at least one active project by a project manager.
| Type | Count | CPU | Memory | Local Usable NVMe Storage | GPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin-CPU | 284 | 2xAMD EPYC 9254 (24 core) | 384 GB | 810 GB | - |
| Fat-CPU | 13 | 2xAMD EPYC 9454 (48 core) | 2304 GB | 1620 GB | - |
| Thin-GPU | 20 | 2xAMD EPYC 9254 (24 core) | 384 GB | 1620 GB | 3xNVIDIA A30 Tensor Core GPU 24GB, 933GB/s |
| Fat-GPU | 7 | 2xAMD EPYC 9454 (48 core) | 1152 GB | 14000 GB | 8xNVIDIA H100 SXM5 GPUs 80GB, 3.35TB/s, connected via NVLink |
To allow for high data transfer rates and low latencies all nodes and servers of Elysium are connected via a Cornelis Omni-Path network. The network topology is a 1:2 blocking fat-tree. Each node is equipped with a single-port Cornelis Omni-Path Express 100Gb/s adapter, except for the Fat-GPU nodes, which have four of these adapters. The Ping-Pong latency for a node-to-node communication with minimal hops is approximately 1.1 μs.
The following file systems are available:
/home: For your software and scripts.
High availability, but no backup.
Quota: 100 GB per user./lustre: Parallel file system to use for your jobs.
High availability, but no backup.
Not for long term storage. Quotas: 4.5 TB and 1,900,000 files per user./tmp: Fast storage on each node for temporary data.
Limited in space, except for FatGPU nodes where multiple TB are available.
Data is removed when the job ends.
For shared jobs the quota scales with the number of reserved cores.Two partitions are available for each type of compute node: the filler partitions are designed for short jobs, while the standard partitions support longer-running tasks.
Jobs in the filler partition have a lower priority and will only start if no job from the regular partition requests resources. Running jobs in the filler will cost only a fraction of the fair share of a regular partition.
The vis partition is special since the visualization nodes are intended for
interactive use only.
| Partition | Timelimit | Nodelist | Max Tasks per Node |
Max Memory per CPU³ | Share-Cost² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cpu | 2-00:00:00¹ | cpu[001-284] | 48 | 8 GB | 1.000 / core |
| cpu_filler | 3:00:00 | cpu[001-336] | 48 | 8 GB | 0.050 / core |
| fat_cpu | 2-00:00:00 | fatcpu[001-013] | 96 | 24 GB | 1.347 / core |
| fat_cpu_filler | 3:00:00 | fatcpu[001-013] | 96 | 24 GB | 0.067 / core |
| gpu | 2-00:00:00 | gpu[001-020] | 48 | 8 GB | 49.374 / GPU |
| gpu_filler | 1:00:00 | gpu[001-020] | 48 | 8 GB | 12.344 / GPU |
| fat_gpu | 2-00:00:00 | fatgpu[001-007] | 96 | 12 GB | 196.867 / GPU |
| fat_gpu_filler | 1:00:00 | fatgpu[001-007] | 96 | 12 GB | 49.217 / GPU |
| vis | 12:00:00 | vis[001-003] | 48 | 24 GB | 5.000 / core |
¹ Times of up to 7 days are possible on this partition but not recommended. Only 2 days are guaranteed, jobs running longer than that may get cancelled if that becomes necessary for important maintenance work.
² Cost does not refer to money, but the factor of computing time that is added to a projects used share in order to compute job priorities. The costs are based on the relative monetary costs of the underlying hardware.
³ Some of the memory is reserved for system services.
Please check the scontrol show partition <partition_name> command
to get the amount of memory that is available for your job
via the --mem-per-cpu=<mem> submission flag.
The HPC resources in Germany are arranged hierarchically in the so-called HPC pyramid.
If suitable for your needs, use the local resources provided by the tier-3 centre. If you need more resources than the local centre can provide, or your project requires specialized hardware, you are welcome to contact another HPC centre or request computing time at a higher tier (tier-2 or tier-1).
Several state-wide tier-2 centres (NHR centres) are available to cater for specialized computing and/or storage requirements. In North Rhine-Westphalia, the RTWH Aachen, the University of Cologne and the University of Paderborn offer structured access to HPC users from NRW institutes.
For extremely complex and data-intensive requirements, HPC resources of the highest tier are available in Germany and the EU. Computing time is only allocated after a technical and scientific peer review process (GCS, PRACE).
We would be happy to advise you on the suitability of your projects as well as provide help with the application process for all levels of the HPC pyramid. Please contact us.
The Ruhr-University of Bochum is part of the North Rhine-Westphalian Competence Network for High Performance Computing HPC.nrw. This network offers a first point of contact and central advisory hub with a broad knowledge base for HPC users in NRW. In addition, the tier-2 centres offer uniform, structured access for HPC users of all universities in NRW, ensuring basic services are provided for locations without tier-3 centres and for Universities of Applied Sciences.
A network of thematic clusters for low-threshold training, consulting and coaching services has been created within the framework of HPC.nrw. The aim is to make effective and efficient use of high-performance computing and storage facilities and to support scientific researchers of all levels. The existing resources and services that the state has to offer are also presented in a transparent way.
According to the Terms of Use, publications must contain an acknowledgement if HPC resources were used. For example:
“Calculations (or parts of them) for this publication were performed on the HPC cluster Elysium of the Ruhr University Bochum, subsidised by the DFG (INST 213/1055-1).”
The RUB University Library helps us maintain a list of such publications, updated in regular intervals:
Access to Elysium is granted based on HPC project applications. If you do scientific work at RUB, you are eligible for access; see the Terms of Use for details.
If you need a user account to login to Elysium go here: Get User Access. Note that access will only be active if you are assigned to at least one HPC project by a project manager!
If you already are a HPC project manager and would like to apply for a new project go here: Apply for a HPC Project.
If you are a professor or research group leader looking to apply for computing resources on Elysium go here: Become Project Manager.
In order to get a user account on Elysium you need to download and fill out the user access application form. Note that you can only login to the cluster after you were assigned to at least one project by a project manager.
RUB LoginID: This is your RUB-LoginID. You need to active two-factor authentication for it.
SSH Key (Pub): Your public (not private!) SSH Key. This key must be your own. Sharing keys with others, e.g. members of your work group is not allowed. You can generate an SSH key pair with the following command:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f ~/.ssh/elysium -N "passphrase"Then you enter the contents of the file ~/.ssh/elysium.pub in the field.
The contents of the file ~/.ssh/elysium.pub should contain one line of text like this one:
ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIOHvm993oC6kwohuHbV0T2xu/x2INIXS2GxFb84s1KbL
alice@laptopIf you used a different tool to generate it, the key might consist of multiple lines and may look like this:
---- BEGIN SSH2 PUBLIC KEY ----
Comment: "eddsa-key-20250910"
AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAJJJ2aNa3e9lOm9NaxIK/7UlDUOPTBCSf0izzFkQJ
M1H1
---- END SSH2 PUBLIC KEY ----The “passphrase” should of course be changed to an appropriately complex password, that prevents malicious usage of your key. Note that you should only do this once. Running the command again, will overwrite your key and block you from accessing the cluster.
Note that RSA keys must have at least 3000 bits in accordance with BSI regulations. We recommend ED25519 keys, as shown in the example above.
After you correctly filled out the form save the PDF as
User-Access-Application_<loginID>.pdf e.g. User-Access-Application_mamuster.pdf
and send it using your RUB-email (not an institute address) to hpc+applications@ruhr-uni-bochum.de
If you want to register another ssh-key or you lost your already registered one, you simply fill out the User-Access-Application again, and send it in with the exact same filename. If your ssh-key was compromised or stolen please notify us immediately so that we can invalidate it.
After you were approved as a Project Manager you can apply for research projects on Elysium by downloading and filling out the project application form. The application is required for managing the fair share of computing resources, and for reporting to the HPC-Beirat, Funding organizations, etc. There is no peer-review process and your project is automatically accepted. Note that more projects do not mean more computing resources. Your personal resources are shared between all you projects.
RUB LoginID: This is your RUB-LoginID.
Project Name: Name under which your project should be listed in any report.
Abstract: A short 2-3 line abstract outlining the contents of your research project. Note that only printable ascii characters are allowed.
Field of Science: Identification number according to DFG subject classification system.
Third-party funded: Optional field for research projects with third party funding. E.g. Funding institution, or project number
RUB LoginIDs: Comma separated list of RUB-LoginIDs of the people you want to participate in this project. (Note that the project manager’s LoginID is not automatically included in the participant list. If you, as a project manager, want to participate in your own project, you must enter your Login ID as well.)
Contingent: From the dropdown menu select the computing resources contingent of your project. If you did not participated in the HPC cluster application you need to select “Miscellaneous User Groups”, or get permission by the members of the other contingents to use their resources.
After you correctly filled out the form save the PDF as
Project-Application_<loginID>_<number>.pdf e.g. Project-Application_mamuster_5.pdf.
The numbering of projects starts at 0 due to technical reasons.
Your first project will have number 0, your second will have number 1, … .
In the example given above the number 5 refers to the sixths project application that was send in by you,
and send it using your RUB-email (not an institute address) to
hpc+applications@ruhr-uni-bochum.de
If you need to add or remove users you can simply modify the user list in the pdf, and send it in again with the exact same filename.
In order to get computing resources on Elysium and be able to manage projects you need to download and fill out the project manager application form and sign the compliance to export control regulations form manually or via RUB Sign.
Please note that only professors and independent group leaders within the Ruhr-University are eligible to becoming project managers! See the regulations for details.
Group Name: The name of your work group. E.g. “Chair for constructive demolition techniques”, or “Computatinal analysis of sumerian poetry”,…
Faculty/Institute: The name of the faculty your group is located in. E.g. “Faculty of Mathematics”, “ICAMS”, or “Universitätsklinikum Josefs-Hospital”
RUB LoginID: This is your RUB-LoginID.
Email: Your RUB-email. (Not your institute email address!) e.g. max.muster@ruhr-uni-bochum.de
Signed export regulations: After you read, understood, and signed the compliance to export control regulations form linked above, you check this box.
After you correctly filled out the form, save the PDF as
Projectmanager-Application_<loginID>.pdf e.g. Resources-Application_mamuster.pdf.
Save a scan of the manually signed, or the via RUB Sign signed export control regulations form as
Compliance-Export-Control-Regulations_<loginID>.pdf e.g.
Compliance-Export-Control-Regulations_mamuster.pdf.
Send the application form and a scan of your signed export control regulations form using your RUB-email (not an institute address) to
hpc+applications@ruhr-uni-bochum.de
Elysium is the central HPC Cluster at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum. See the overview of its resources.
To use Elysium, you need to
Please read about the basic concept of using Elysium first.
The login process combines SSH key-based authentication with web-based two-factor authentication.
After login, you can use available software modules or build your own software.
Read about submitting jobs and allocating resources in the SLURM section.
Elysium provides four login nodes: login1.elysium.hpc.rub.de, …, login4.elysium.hpc.rub.de.
These are your entry points to the cluster.
After login, you typically use them to prepare your software and copy your data to the appropriate locations. Performing calculations on the login nodes is prohibited (see FAQ).
You can then allocate resources on the cluster using the Slurm workload manager.
After submitting your request, Slurm will grant you the resources as soon as they are free and your priority is higher than the priority of other jobs that might be waiting for some of the same resources.
Your priority depends on your waiting time and your remaining FairShare.
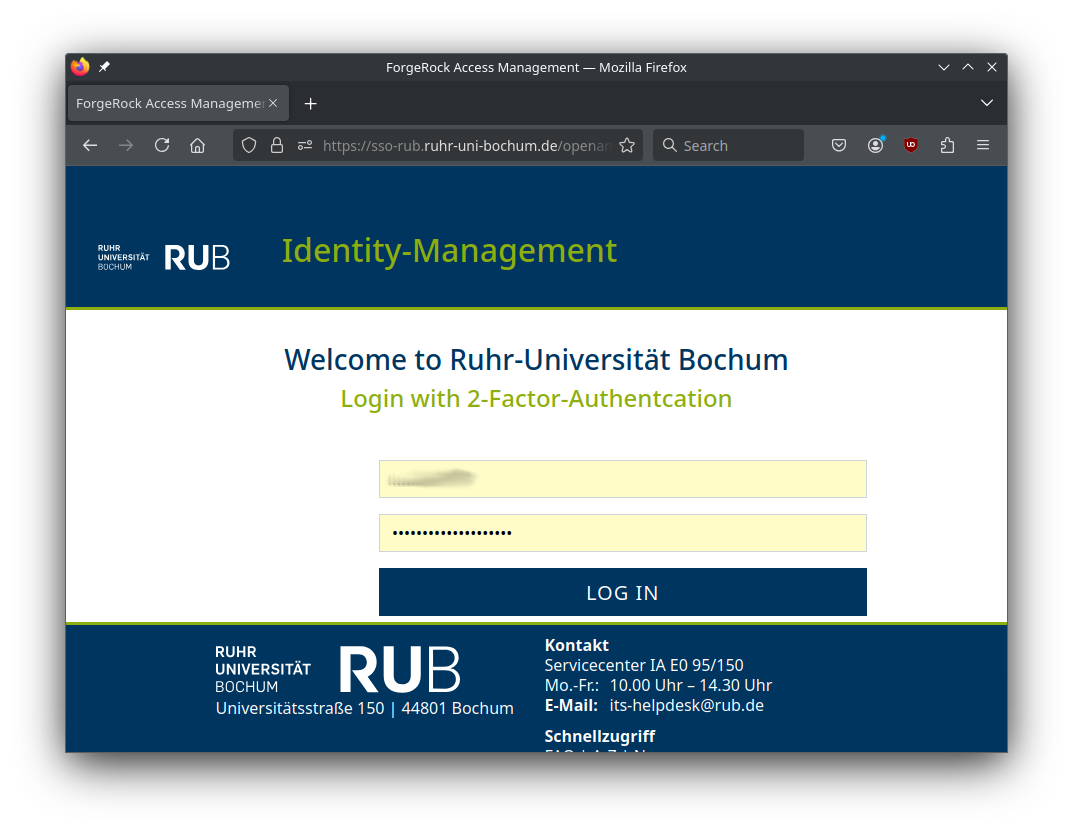
Login to Elysium combines the common SSH key-based authentication with web-based two-factor authentication.
Circumventing these steps (e.g., opening sessions without the need for two factor authentication, sharing of accounts, keys, or login credentials) violates the IT.SERVICES Terms of Use and may result in permanent loss of access rights to the Elysium cluster and/or other services provided by IT.SERVICES.
In order to be able to authenticate during login you need submit your public SSH key via the User Access Application Form as well as enable two-factor authentication for your RUB LoginID at rub.de/login.
The additional web-based authentication is cached for 14 hours so that you typically only have to do it once per work day, per login node, and per IP address you connect from. After that, your normal key-based SSH workflow will work as expected.
In order to simplify the use of SSH keys we recommend to specify it as identity file in your SSH config.
This can be done by adding the following lines to your ~/.ssh/config file:
Host login00*.elysium.hpc.rub.de login00*.elysium.hpc.ruhr-uni-bochum.de
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/elysium
User <loginID>where <loginID> has to be exchanged by your RUB LoginID.
If your SSH key is located in a different file the IdentityFile path needs to be adjusted accordingly.
Follow these steps:
Start ssh with the correct private key, your RUB LoginID, and one of the four login hosts, e.g.
ssh -i ~/.ssh/elysium LOGINID@login001.elysium.hpc.ruhr-uni-bochum.de,
or
ssh login001.elysium.hpc.rub.de if you want to use the SSH config specified above.
Available login nodes are login001 to login004.
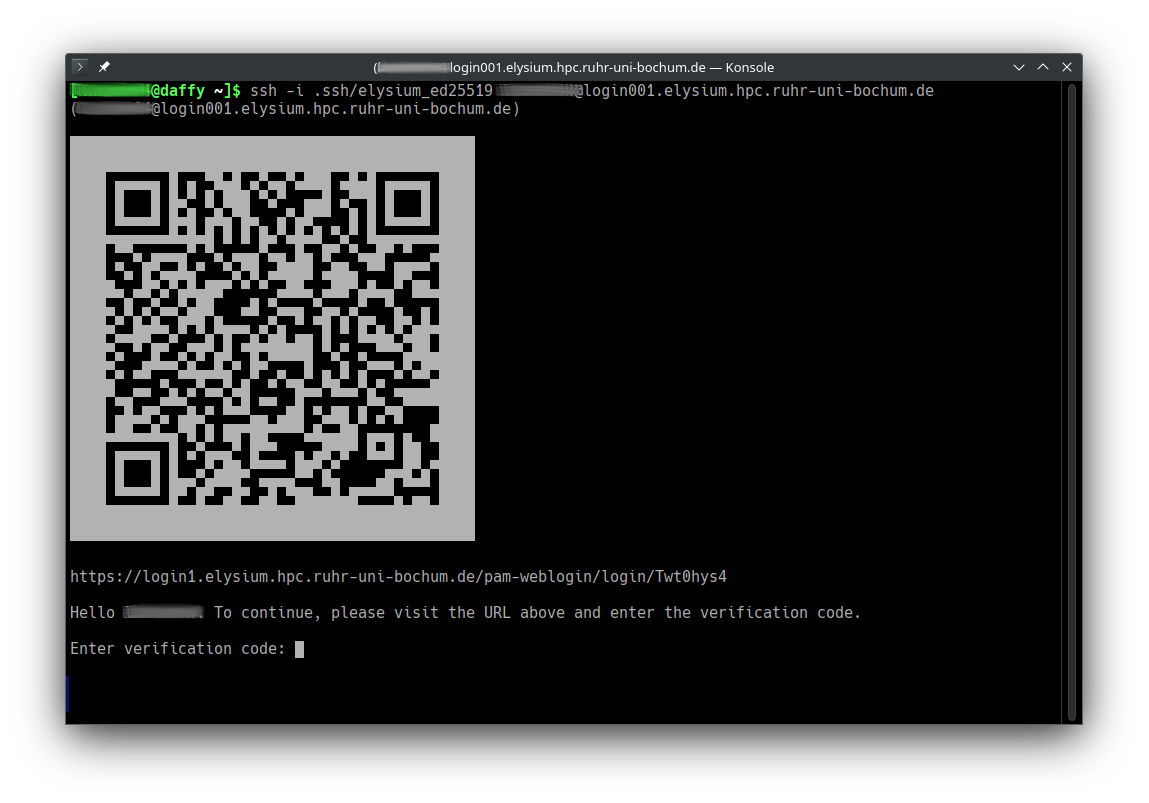

Open the URL in a browser (or scan the QR code with your smartphone) to start web-based two-factor authentication.

After successful login, you get a four-digit verification code.
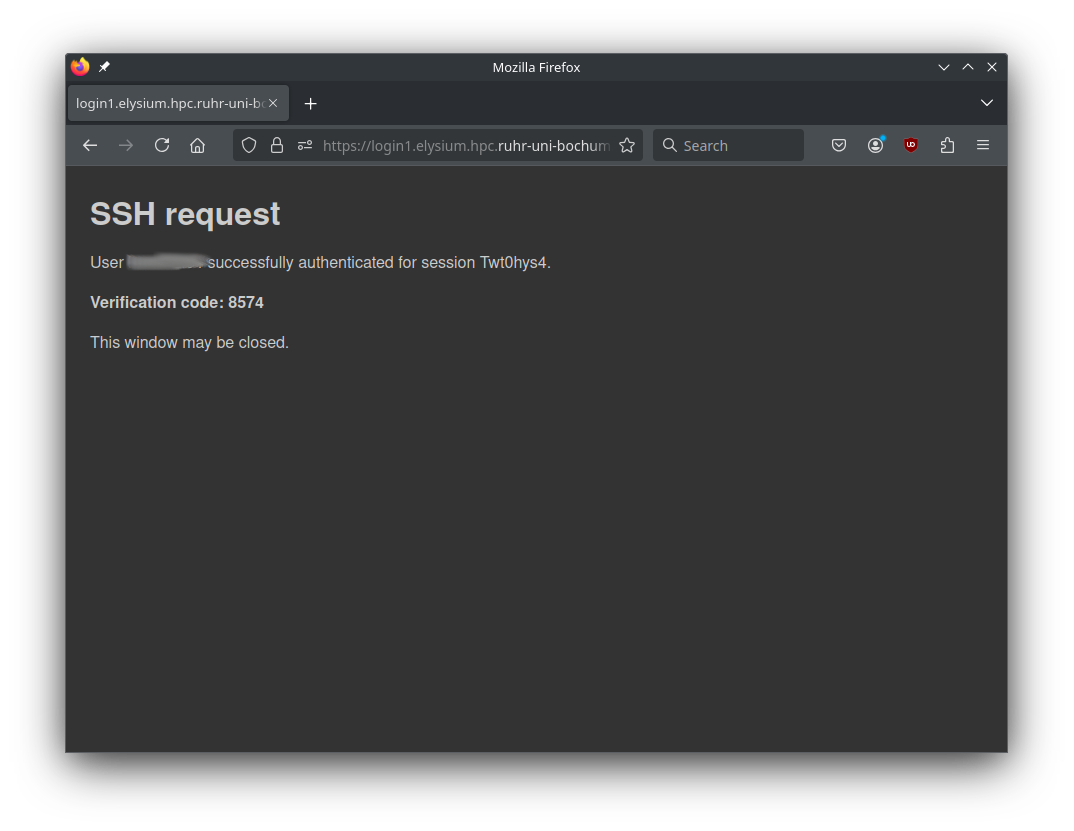

For the next 14 hours, only step 1 (classic key-based authentication) will be necessary on the chosen login node for the IP address you connected from.
Login will fail if:
We provide a basic set of toolchains and some common libraries via modules.
To build common HPC software packages, we provide a central installation of the Spack package manager. A detailed guide on how to use this installation can be found in the Spack Usage Guide.
We use the Lmod module system:
module available (shortcut ml av) lists available modulesmodule load loads selected modulesmodule list shows modules currently loaded in your environmentThere are also hidden modules that are generally less relevant to users but can
be viewed with ml --show_hidden av.
We are committed to providing the tools you need for your research and development efforts. If you require modules that are not listed here or need different versions, please contact our support team, and we will be happy to assist you.
We use the Spack package manager to provide a collection of common HPC software packages. This page explains how to use the central Spack installation to build your own modulefiles.
rub-deploy-spack-configsYou can directly copy the configuration files described in Central Spack Installation (upstreams.yaml, config.yaml, modules.yaml, compilers.yaml) to your home directory using the rub-deploy-spack-configs command:
rub-deploy-spack-configsAdd these lines to your ~/.bashrc to activate spack with every login:
export MODULEPATH=$MODULEPATH:$HOME/spack/share/spack/lmod/linux-almalinux9-x86_64/Core
. /cluster/spack/0.23.0/share/spack/setup-env.shBelow is a detailed guide on how to effectively use Spack.
To find available packages, use:
spack list <keyword> # Search for packages by name
# Example:
spack list openfoam
openfoam openfoam-org
==> 2 packagesFor detailed information about a package:
spack info <package> # Show versions, variants, and dependencies
# Example:
spack info hdf5For a quick search for all available packages in spack, visit https://packages.spack.io/.
Variants are build options that enable or disable features. List them with spack info <package>:
spack info hdf5Output includes:
Preferred version:
1.14.3 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.14/hdf5-1.14.3/src/hdf5-1.14.3.tar.gz
Safe versions:
1.14.3 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.14/hdf5-1.14.3/src/hdf5-1.14.3.tar.gz
1.14.2 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.14/hdf5-1.14.2/src/hdf5-1.14.2.tar.gz
1.14.1-2 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.14/hdf5-1.14.1-2/src/hdf5-1.14.1-2.tar.gz
1.14.0 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.14/hdf5-1.14.0/src/hdf5-1.14.0.tar.gz
1.12.3 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.12/hdf5-1.12.3/src/hdf5-1.12.3.tar.gz
1.12.2 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.12/hdf5-1.12.2/src/hdf5-1.12.2.tar.gz
1.12.1 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.12/hdf5-1.12.1/src/hdf5-1.12.1.tar.gz
1.12.0 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.12/hdf5-1.12.0/src/hdf5-1.12.0.tar.gz
1.10.11 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.10/hdf5-1.10.11/src/hdf5-1.10.11.tar.gz
1.10.10 https://support.hdfgroup.org/ftp/HDF5/releases/hdf5-1.10/hdf5-1.10.10/src/hdf5-1.10.10.tar.gz
Variants:
api [default] default, v110, v112, v114, v116, v16, v18
Choose api compatibility for earlier version
cxx [false] false, true
Enable C++ support
fortran [false] false, true
Enable Fortran support
hl [false] false, true
Enable the high-level library
mpi [true] false, true
Enable MPI supportDefaults are shown in square brackets, possible values to the right.
To see which dependencies will be installed, use:
spack spec hdf5Output includes:
Input spec
--------------------------------
- hdf5
Concretized
--------------------------------
[+] hdf5@1.14.3%gcc@11.4.1~cxx~fortran+hl~ipo~java~map+mpi+shared~subfiling~szip~threadsafe+tools api=default build_system=cmake build_type=Release generator=make patches=82088c8 arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^cmake@3.27.9%gcc@11.4.1~doc+ncurses+ownlibs build_system=generic build_type=Release arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^curl@8.7.1%gcc@11.4.1~gssapi~ldap~libidn2~librtmp~libssh+libssh2+nghttp2 build_system=autotools libs=shared,static tls=mbedtls,openssl arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^libssh2@1.11.0%gcc@11.4.1+shared build_system=autotools crypto=mbedtls patches=011d926 arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^xz@5.4.6%gcc@11.4.1~pic build_system=autotools libs=shared,static arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^mbedtls@2.28.2%gcc@11.4.1+pic build_system=makefile build_type=Release libs=shared,static arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^nghttp2@1.52.0%gcc@11.4.1 build_system=autotools arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^diffutils@3.10%gcc@11.4.1 build_system=autotools arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^openssl@3.3.0%gcc@11.4.1~docs+shared build_system=generic certs=mozilla arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^ca-certificates-mozilla@2023-05-30%gcc@11.4.1 build_system=generic arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^ncurses@6.5%gcc@11.4.1~symlinks+termlib abi=none build_system=autotools patches=7a351bc arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^gcc-runtime@11.4.1%gcc@11.4.1 build_system=generic arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[e] ^glibc@2.34%gcc@11.4.1 build_system=autotools arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^gmake@4.4.1%gcc@11.4.1~guile build_system=generic arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4
[+] ^openmpi@5.0.3%gcc@11.4.1~atomics~cuda~gpfs~internal-hwloc~internal-libevent~internal-pmix~java+legacylaunchers~lustre~memchecker~openshmem~orterunprefix~romio+rsh~static+vt+wrapper-rpath build_system=autotools fabrics=ofi romio-filesystem=none schedulers=slurm arch=linux-almalinux9-zen4It’s always a good idea to check the specs before installing.
Control variants with + (enable) or ~ (disable):
spack install hdf5 +mpi +cxx ~hl # Enable MPI and C++, disable high-level APIFor packages with CUDA, use compute capabilities 8.0 (for GPU nodes) and 9.0 (for FatGPU nodes):
spack install openmpi +cuda cuda_arch=80,90Use % to specify a compiler. Check available compilers with:
spack compilersExample:
spack install hdf5 %gcc@11.4.1When using compilers other than GCC 11.4.1, dependencies must also be built with that compiler:
spack install --fresh hdf5 %gcc@13.2.0Use ^ to specify dependencies with versions or variants:
spack install hdf5 ^openmpi@4.1.5Dependencies can also have variants:
spack install hdf5 +mpi ^openmpi@4.1.5 +threads_multipleMake sure to set the variants for the package and the dependencies on the right position or installation will fail.
Combine options for customized installations:
spack install hdf5@1.14.3 +mpi ~hl ^openmpi@4.1.5 +cuda cuda_arch=80,90 %gcc@11.4.1Install a new compiler (e.g., GCC 13.2.0) with:
spack install gcc@13.2.0Add it to Spack’s compiler list:
spack compiler add $(spack location -i gcc@13.2.0)Verify it’s recognized:
spack compilersUse it to build packages:
spack install --fresh hdf5 %gcc@13.2.0If you have multiple installations of the same package with different variants, you can inspect their configurations using Spack’s spec command or the find tool.
Use spack find -vl to show all installed variants and their hashes:
spack find -vl hdf5
-- linux-almalinux9-zen4 / gcc@11.4.1 ---------------------------
amrsck6 hdf5@1.14.3~cxx~fortran+hl~ipo~java~map+mpi+shared~subfiling~szip~threadsafe+tools api=default build_system=cmake build_type=Release generator=make patches=82088c8
2dsgtoe hdf5@1.14.3+cxx+fortran~hl~ipo~java~map+mpi+shared~subfiling~szip~threadsafe+tools api=default build_system=cmake build_type=Release generator=make patches=82088c8
==> 2 installed packagesamrsck6 and 2dsgtoe are the unique hashes for each installation.+hl while the other does not.Use spack spec /<hash> to view details of a specific installation:
spack spec /amrsck6
spack spec /2dsgtoe To compare variants between two installations, use spack diff with both hashes:
spack diff /amrsck6 /2dsgtoeYou will see a diff in the style of git:
--- hdf5@1.14.3/amrsck6mml43sfv4bhvvniwdydaxfgne
+++ hdf5@1.14.3/2dsgtoevoypx7dr45l5ke2dlb56agvz4
@@ virtual_on_incoming_edges @@
- openmpi mpi
+ mpich mpiSo one version depends on OpenMPI while the other depends on MPICH.
For multiple variants of a package, specify the hash:
spack uninstall /amrsck6Activate the central Spack installation with:
source /cluster/spack/0.23.0/share/spack/setup-env.shUse it as a starting point for your own builds without rebuilding everything from scratch.
Add these files to ~/.spack:
~/.spack/upstreams.yaml:
upstreams:
central-spack:
install_tree: /cluster/spack/opt~/.spack/config.yaml:
config:
install_tree:
root: $HOME/spack/opt/spack
source_cache: $HOME/spack/cache
license_dir: $HOME/spack/etc/spack/licenses~/.spack/modules.yaml:
modules:
default:
roots:
lmod: $HOME/spack/share/spack/lmod
enable: [lmod]
lmod:
all:
autoload: direct
hide_implicits: true
hierarchy: []Add these lines to your ~/.bashrc:
export MODULEPATH=$MODULEPATH:$HOME/spack/share/spack/lmod/linux-almalinux9-x86_64/Core
. /cluster/spack/0.23.0/share/spack/setup-env.shThen run:
spack compiler findCreate ~/.spack/repos.yaml:
repos:
- $HOME/spack/var/spack/reposAnd a local repo description in ~/spack/var/spack/repos/repo.yaml:
repo:
namespace: overridesCopy and edit a package definition, e.g., for ffmpeg:
cd ~/spack/var/spack/repos/
mkdir -p packages/ffmpeg
cp /cluster/spack/0.23.0/var/spack/repos/builtin/packages/ffmpeg/package.py packages/ffmpeg
vim packages/ffmpeg/package.pyAlternatively, you can use a fully independent Spack installation in your home directory or opt for EasyBuild.
Vampir is a framework for analyzing program behavior of serial and parallel software by utilizing function instrumentation via Score-p. Vampir is licensed by HPC.nrw and can be used freely on the Elysium Cluster. This site merely shows a small test case to show how Score-p can be used to generate profiling data and how Vampir can be started on Elysium. For information how to use Vampir to analyze your application, extract useful performance metrics, and identify bottlenecks, please refer to the Score-p Cheat Sheet and the official Vampir Documentation.
In order to generate profiling data the function calls in the application need to be instrumented. This means inserting additional special function calls that record the time, current call stack, and much more. Fortunately, this is not done manually, but can easily achieved by using the Score-p compiler wrapper. To follow along you can use this MPI Example Code.
To use the Score-p compiler wrapper, all that is needed is to prepend the compiler by the scorep command:
module load openmpi/5.0.5-d3ii4pq
module load scorep/8.4-openmpi-5.0.5-6mtx3p6
scorep mpicc -o mpi-test.x mpi-test.cIn the case of a Makefile, or other build systems, the compiler variable has to be adjusted accordingly.
Profiling data is created by running the application. Note that the profiling files can grow to enormous sizes. Thus, it is advisable to choose a small representative test case for your application and not a full production run. In its default mode Score-p collects profiling data by sampling the applications call-stack from time to time. In order to generate an accurate profile tracing needs to be enabled in your job script:
module load openmpi/5.0.5-d3ii4pq
module load scorep/8.4-openmpi-5.0.5-6mtx3p6
export SCOREP_ENABLE_TRACING=true
mpirun -np 4 ./mpi-test.xHere is a full job script for the example:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --partition=cpu
#SBATCH --ntasks=4
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --account=<Account>
#SBATCH --time=00-00:05:00
module purge
module load openmpi/5.0.5-d3ii4pq
module load scorep/8.4-openmpi-5.0.5-6mtx3p6
export SCOREP_ENABLE_TRACING=true
mpirun -np 4 ./mpi-test.xThe execution of the instrumented application will take significantly longer than usual.
Thus, it should never be used for production runs, but merely for profiling.
After the application is finished a new directory was created, containing the time stamp and some other information in its name e.g.: scorep-20251222_0912_1523094386395226
The file traces.otf2 contains the profiling data required by Vampir.
In order to visualize the profiling data a Visualization Session has to be established. Vampir can be started with
module load vampir
vglrun +pr -fps 20 vampir ./traces.otf2On Elysium, VASP can be built with Spack using:
spack install vasp@6.4.3 +openmp +fftlib ^openmpi@5.0.5 ^fftw@3+openmp ^intel-oneapi-mkl threads=openmp +ilp64This configuration uses:
We choose MKL as baseline because it is the de-facto HPC standard and performs well on AMD EPYC when AVX512 code paths are enabled.
Intel’s MKL only enables AVX512 optimisations on Intel CPUs. On AMD, MKL defaults to AVX2/SSE code paths.
To unlock the faster AVX512 kernels on AMD EPYC we provide libfakeintel, which fakes Intel CPUID flags.
| MKL version | library to preload | |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 2024.x | /lib64/libfakeintel.so |
|
| ≥ 2025.x | /lib64/libfakeintel2025.so |
works for older versions too |
⚠ Intel gives no guarantee that all AVX512 instructions work on AMD CPUs. In practice, the community has shown that not every kernel uses full AVX512 width, but the overall speed-up is still substantial.
Activate AVX512 by preloading the library in your job:
export LD_PRELOAD=/lib64/libfakeintel2025.so:${LD_PRELOAD}This benchmark uses a 256-atom silicon supercell (Si256) with the HSE06 hybrid functional.
Hybrid DFT combines FFT-heavy parts with dense BLAS/LAPACK operations and is therefore a good proxy for most large-scale electronic-structure workloads.
| Configuration | Time [s] | Speed-up vs baseline |
|---|---|---|
| MKL (no AVX512) | 2367 | 1.00× |
| MKL (+ AVX512) | 2017 | 1.17× |
→ Always enable AVX512.
The baseline DFT case runs 17 % faster with libfakeintel,
AOCL (AMD Optimized Libraries) is AMD’s analogue to MKL, providing:
Build example:
spack install vasp@6.4.3 +openmp +fftlib %aocc ^amdfftw@5 ^amdblis@5 threads=openmp ^amdlibflame@5 ^amdscalapack@5 ^openmpiAOCL detects AMD micro-architecture automatically and therefore does not require libfakeintel.
| Configuration | Time [s] | Speed-up vs baseline |
|---|---|---|
| MKL (+ AVX512) | 2017 | 1.00 |
| AOCL (AMD BLIS / libFLAME) | 1919 | 1.05 |
The AOCl build is another 5% faster than MKL with AVX512 enabled.
Each compute node has two EPYC 9254 CPUs with 24 cores each (48 total). Each CPU is subdivided into 4 NUMA domains with separate L3 caches and memory controllers.
This L3-hybrid layout increases memory locality, because each rank mainly uses its own local memory and avoids cross-socket traffic.
| Configuration | Time [s] | Speed-up vs MPI-only |
|---|---|---|
| MKL (L3 hybrid) | 1936 | 1.04× |
| AOCL (L3 hybrid) | 1830 | 1.05× |
Hybrid L3 adds a modest 4-5 % speed-up.
| Configuration | Nodes | Time [s] | Speed-up vs 1-node baseline |
|---|---|---|---|
| MKL MPI-only | 2 | 1305 | 1.55× |
| AOCL MPI-only | 2 | 1142 | 1.68× |
| MKL L3 hybrid | 2 | 1147 | 1.69× |
| AOCL L3 hybrid | 2 | 968 | 1.89× |
Interpretation
AOCL shows the strongest scaling across nodes; MKL’s hybrid variant catches up in scaling compared to its MPI-only counterpart. The L3-hybrid layout maintains efficiency even in the multi-node regime.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -J vasp_aocl_l3hyb
#SBATCH -N 1
#SBATCH --ntasks=8
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=6
#SBATCH -p cpu
#SBATCH -t 48:00:00
#SBATCH --exclusive
module purge
module load vasp-aocl
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=6
export OMP_PLACES=cores
export OMP_PROC_BIND=close
export BLIS_NUM_THREADS=6
mpirun -np 8 --bind-to l3 --report-bindings vasp_std#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -J vasp_mkl_avx512_l3hyb
#SBATCH -N 1
#SBATCH --ntasks=8
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=6
#SBATCH -p cpu
#SBATCH -t 48:00:00
#SBATCH --exclusive
module purge
module load vasp-mkl
export LD_PRELOAD=/lib64/libfakeintel2025.so:${LD_PRELOAD}
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=6
export OMP_PLACES=cores
export OMP_PROC_BIND=close
export MKL_NUM_THREADS=6
export MKL_DYNAMIC=FALSE
mpirun -np 8 --bind-to l3 --report-bindings vasp_stdThe XAS Mn-in-ZnO case models a core-level excitation (X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy). These workloads are not FFT-dominated; instead they involve many unoccupied bands and projector evaluations.
| Configuration | Time [s] | Relative |
|---|---|---|
| MKL MPI-only | 897 | 1.00× |
| AOCL MPI-only | 905 | 0.99× |
| MKL L3 hybrid | 1202 | 0.75× |
| AOCL L3 hybrid | 1137 | 0.79× |
| Configuration | Nodes | Time [s] | Relative |
|---|---|---|---|
| MKL MPI-only | 2 | 1333 | 0.67× |
| AOCL MPI-only | 2 | 1309 | 0.69× |
| MKL L3 hybrid | 2 | 1366 | 0.66× |
| AOCL L3 hybrid | 2 | 1351 | 0.67× |
Interpretation
For core-level / XAS calculations, hybrid OpenMP parallelisation is counter-productive, and scaling beyond one node deteriorates performance due to load imbalance and communication overhead.
OMP_NUM_THREADS=1 to avoid unwanted OpenMP activity.For optimal performance on Elysium with AMD EPYC processors, we recommend using the AOCL build as the default choice for all VASP workloads. AOCL consistently outperforms or matches MKL (+AVX512) across tested scenarios (e.g., 5 % faster for Si256 single-node, up to 1.89× speedup for multi-node scaling) and does not require additional configuration like libfakeintel. However, MKL remains a robust alternative, especially for users requiring compatibility with existing workflows.
| Workload type | Characteristics | Recommended setup |
|---|---|---|
| Hybrid DFT (HSE06, PBE0, etc.) | FFT + dense BLAS, OpenMP beneficial | AOCL L3 Hybrid (8×6) |
| Standard DFT (PBE, LDA) | light BLAS, moderate FFT | AOCL L3 Hybrid or MPI-only |
| Core-level / XAS / EELS | many unoccupied bands, projectors | AOCL MPI-only (single-node) |
| MD / AIMD (>100 atoms) | large FFTs per step | AOCL L3 Hybrid |
| Static small systems (<20 atoms) | few bands, small matrices | AOCL MPI-only |
Recommendations:
libfakeintel2025.so to enable AVX512 optimizations.MPI-only and L3 Hybrid on one node to determine the optimal configuration for your specific system.The Elysium HPC system utilizes SLURM as a resource manager, scheduler, and accountant in order to guarantee fair share of the computing resources.
If you are looking for technical details regarding the usage and underlying mechanisms of SLURM we recommend participating in the Introduction to HPC training course.
Examples of job scripts for different job types that are tailored to the Elysium cluster can be found in the Training Section.
All nodes in the Elysium cluster are grouped by their hardware kind, and job submission type. This way users can request specific computing hardware, and multi node jobs are guaranteed to run on nodes with the same setup.
In order to get a list of the available partitions, their current state,
and available nodes, the sinfo command can be used.
1[login_id@login001 ~]$ sinfo
2PARTITION AVAIL TIMELIMIT NODES STATE NODELIST
3cpu up 7-00:00:00 4 alloc cpu[033-034,037-038]
4cpu up 7-00:00:00 280 idle cpu[001-032,035-036,039-284]
5cpu_filler up 3:00:00 4 alloc cpu[033-034,037-038]
6cpu_filler up 3:00:00 280 idle cpu[001-032,035-036,039-284]
7fat_cpu up 2-00:00:00 13 idle fatcpu[001-013]
8fat_cpu_filler up 3:00:00 13 idle fatcpu[001-013]
9gpu up 2-00:00:00 20 idle gpu[001-020]
10gpu_filler up 1:00:00 20 idle gpu[001-020]
11fat_gpu up 2-00:00:00 1 drain* fatgpu005
12fat_gpu up 2-00:00:00 5 mix fatgpu[001,003-004,006-007]
13fat_gpu up 2-00:00:00 1 idle fatgpu002
14fat_gpu_filler up 1:00:00 1 drain* fatgpu005
15fat_gpu_filler up 1:00:00 5 mix fatgpu[001,003-004,006-007]
16fat_gpu_filler up 1:00:00 1 idle fatgpu002
17vis up 1-00:00:00 3 idle vis[001-003]SLURM provides two commands to request resources.
srun is used to start an interactive session.
1[login_id@login001 ~]$ srun -N 1 --partition=cpu --job-name=test --time=00:05:00 --account=testproj_0000 --pty bash
2[login_id@cpu001 ~]$sbatch is used to request resources that will execute a job script.
1[login_id@login001 ~]$ sbatch -N 1 --partition=cpu --job-name=test --time=00:05:00 --account=testproj_0000 myscript.sh
2Submitted batch job 10290For sbatch the submission flags can also be incorporated into the job script itself.
More information about job scripts, and the required and some optional flags can be found
in the Training/SLURM Header section.
On Elysium several flags are mandatory.
sbatch and srun will refuse to queue the job
and give a detailed explanation which flag is missing
and how to incorporate it into your command or script.
Use spredict myscript.sh to estimate the start time of your job.
All nodes are shared by default.
If a user requests fewer CPU-cores than a node provides, other users may use these resources at the same time.
To ensure that the requested nodes are not shared use the --exclusive flag.
If more than one node is requested the --exlusive flag is mandatory.
For requesting resources on a GPU node the --gpus=<number of GPUs> flag is required.
In order to allow for fairly shared resources the number of CPUs per GPU is limited.
Thus the --cpus-per-gpu=<number of CPU cores per GPU> is required as well.
For multi node jobs --gpus-per-node=<number of GPUs per node> option needs to be set.
For requesting resources on a visualization node no --gpu parameter is needed.
The available GPU will automatically be shared between all jobs on the node.
If requested resources are currently not available, jobs are queued
and will start as soon as the resources are available again.
To check which jobs are currently running,
and which ones are pending and for what reason the
squeue command can be used.
For privacy reasons only the user’s own jobs are displayed.
1[login_id@login001 ~]$ squeue
2 JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
3 10290 cpu test login_id R 2:51 1 cpu001Users/Projects/Groups/Institutes are billed for computing resources used.
To check how many resources a user is entitled to
and how many they have already used the sshare command is used.
For privacy reasons only the user’s own shares are displayed.
1[login_id@login001 ~]$ sshare
2Account User RawShares NormShares RawUsage EffectvUsage FairShare
3-------------------- ---------- ---------- ----------- ----------- ------------- ----------
4testproj_0000 login_id 1000 0.166667 20450435 0.163985 0.681818Due to technical reasons the project names on Elysium have rather cryptic names,
based on the loginID of the project manager and a number.
In order to make it easier to select a project account for the
--account flag for srun, or sbatch,
and to check the share and usage of projects,
the RUB-exclusive rub-acclist command can be used.
1[login_id@login001 ~]$ rub-acclist
2Project ID | Project Description
3--------------+--------------------------------------------------
4testproj_0000 | The fundamental interconnectedness of all things
5testproj_0001 | The translated quaternion for optimal pivotingWe provide Visualization via VirtualGL on the visualization nodes on Elysium.hpc.ruhr-uni-bochum.de
X11 server with 24-bit- or 32-bit Visuals. VirtualGL version > 3.0.2 installed.
You can check support for your Operating Sytsem at: https://virtualgl.org/Documentation/OSSupport You can download VirtualGL at: https://github.com/VirtualGL/virtualgl/releases
To use VirtualGL on Elysium, you will only need the VirtualGL client, it is not necessary to configure a VirtualGL Server.
Allocate resources in the vis partition.
salloc -p vis -N1 --time=02:00:00 --account=$ACCOUNTThis will allocate a share of one vis node for 2 hours. (For more options on node allocations see SLURM). Wait until a Slot in the vis partition is available. You can check if your resources are already allocated using the ‘squeue’ command.
Connect directly from your computer to the visualization node via ssh with vglonnect -s Use one of the login servers login[001-004] as a jump host.
vglconnect -s $HPCUSER@vis001.elysium.hpc.rub.de -J $HPCUSER@login001.elysium.hpc.rub.deIf you are prompted for password, enter your RUB-password. If you don’t like long commands, you can configure one of the login nodes as jump host in your ~/.ssh/config for the vis[001-003] hosts. The command vglconnect -s accepts nearly the same syntax as ssh.
Load a module if required. Start your application using vglrun, please remember to use useful command line options like -fps .
module load vmd
vglrun +pr -fps 60 vmdPlease remember to cancel the resource allocation once you are done with your interactive session.
scancel $jobIDThe Elysium cluster provides the possibility to work interactively to allow compute intensive preparations, post processing steps, or tests. Further, interactive sessions on the visualization nodes (vis[001-003]) allow for remote connections to run e.g. jupyter notebooks from your local machine.
In order to reserve nodes interactively the following command should be used:
[login_id@login001 ~]$ srun -N 1 --partition=vis --job-name=interactive --time=01:00:00 --tasks-per-node=1 --account=<project_name> --pty bashDepending on the load on the cluster it might take some time
until resources can be allocated for your job.
Even if resources are free the scheduler might need a
few seconds to reserve the requested node.
If you require a specific node for your interactive
session you may utilize the -w <nodename> flag.
Note that this might increase the time for your session
to start until the requested node is available.
(For more options on node allocations see SLURM).
As long as you have any job running on the target node you can use ssh to connect from any login node to your target node. When the job terminates, all ssh connections will be terminated as well.
Connection to compute nodes from local machines is only possible for the three visualization nodes (vis[001-003]). In order to allow a local machine to connect to a node with an active job, one of the login nodes needs to be defined as a jump host, to forward your ssh request.
Please make sure that the ~/.ssh/config on your local machine
contains the following entries:
Host elysium-login001
User <login_id>
Hostname login001.elysium.hpc.rub.de
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/elysium
Host *.elysium.hpc.rub.de *.elysium.hpc.ruhr-uni-bochum.de !login*.elysium.hpc.rub.de !login*.elysium.hpc.ruhr-uni-bochum.de
User <login_id>
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/elysium
ProxyJump elysium-login001Please ensure that the IdentityFile points to the correct (private) key.
You are now able to connect to connect to one of the vis nodes with the following command:
[localuser@localmachine ~]$ ssh vis001.elysium.hpc.rub.de
[<login_id>@vis001 ~]$With our web-based job monitoring system (ClusterCockpit), you can easily monitor and analyze the performance of your jobs on the Elysium HPC system. For a quick performance check, see Metrics to Check; for an in-depth analysis, refer to the HPC-Wiki. For details on the web interface, consult the official documentation.
To access the job monitoring system, use your RUB LoginID and corresponding password as credentials.

After logging in successfully, you will see the “Clusters” overview, which displays the total number of jobs you have run and the current number of jobs running on the cluster.
At present, this information includes only the Elysium cluster.
You can continue from here, either by going to the total jobs overview, or the running jobs overview.
Alternatively, you can click on “My Jobs” in the top left of the page, or search for job names/ids in the top right of the page.

The “My Jobs” page displays a list of your jobs, fully customizable to your requirements. Use the menus in the top left corner to sort or filter the list, and select the metrics you want to display for your jobs. Below, you’ll find a detailed table with job IDs, names, and your selected metrics.
This page is split into three sections. The first one shows general information: JobInfo, a footprint and a roofline diagram that shows how efficiently the job utilized the hardware. Note that the footprint is only updated every 10 minutes and the energy footprint is generated after the job finished.
In the next section some metrics are shown as diagrams. For some of the diagrams you can choose the scope, i.e. core, socket or node. The shown metrics and their order can be customized with the “Select Metrics” menu. This selection is saved per partition. Double-click the graph to zoom out if the scale is too small.
The last section displays selected metrics in a numerical way, lets you inspect your job script, and shows more detail about the job allocation an runtime parameters.
The following table shows the metrics which are available for jobs on Elysium:
| Metric name | Meaning | Meaningful for shared jobs |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | ||
| cpu_load | Load on the node (processes/threads requesting CPU time) | No |
| cpu_load_core | Load on CPU cores of a job (processes/threads per core) | Yes |
| cpu_user | Percentage of CPU time spent as user time for each CPU core | Yes |
| clock | Frequency of the CPU cores of the job | Yes (affected by other jobs) |
| ipc | Instructions per cycle | Yes |
| flops_any | Floating-point operations performed by CPU cores | Yes |
| core_power | Power consumption of individual CPU cores | Yes |
| Memory | ||
| mem_bw | Memory bandwidth | No (full socket only) |
| mem_used | Main memory used on the node | No |
| job_mem_used | Main memory used for the job | Yes |
| disk_free | Free disk space on the node | No |
| GPU | ||
| nv_compute_processes | Number of processes using the GPU | Yes |
| acc_mem_used | Accelerator (GPU) memory usage | Yes |
| acc_mem_util | Accelerator (GPU) memory utilization | Yes |
| acc_power | Accelerator (GPU) power usage | Yes |
| acc_utilization | Accelerator (GPU) compute utilization | Yes |
| Filesystem | ||
| lustre_write_bw | /lustre write bandwidth | No |
| lustre_read_bw | /lustre read bandwidth | No |
| lustre_close | /lustre file close requests | No |
| lustre_open | /lustre file open requests | No |
| lustre_statfs | /lustre file stat requests | No |
| io_reads | Local Disk I/O read operations/s | No |
| io_writes | Local Disk I/O write operations/s | No |
| nfs4_close | /home + /cluster file close requests | No |
| nfs4_open | /home + /cluster file open requests | No |
| nfsio_nread | /home I/O read bandwidth | No |
| nfsio_nwrite | /home I/O write bandwidth | No |
| Network | ||
| ib_recv | Omnipath receive bandwidth | No |
| ib_xmit | Omnipath transmit bandwidth | No |
| ib_recv_pkts | Omnipath received packets/s | No |
| ib_xmit_pkts | Omnipath transmitted packets/s | No |
| net_bytes_in | Ethernet incoming bandwidth | No |
| net_bytes_out | Ethernet outgoing bandwidth | No |
| net_pkts_in | Ethernet incoming packets/s | No |
| net_pkts_out | Ethernet outgoing packets/s | No |
| NUMA Nodes | ||
| numastats_numa_hit | NUMA hits/s | No |
| numastats_numa_miss | NUMA misses/s | No |
| numastats_interleave_hit | NUMA interleave hits/s | No |
| numastats_local_node | NUMA local node accesses/s | No |
| numastats_numa_foreign | NUMA foreign node accesses/s | No |
| numastats_other_node | NUMA other node accesses/s | No |
| Node metrics | ||
| node_total_power | Power consumption of the whole node | No |
For a quick performance analysis, here are some key metrics to review:
cpu_user: Should be close to 100%. Lower values indicate system processes are using some of your resources.flops_any: Measures calculations per second. On Elysium, a typical CPU node averages around 400 GFLOPS.cpu_load_core: Should be 1 at most for non-OpenMP jobs. Higher values suggest oversubscription.ipc: Instructions executed per cycle. Higher values indicate better efficiency.mem_bw: Memory bandwidth, maxing out at 350 GByte/s. Only meaningful if the node isn’t shared or your job uses a full socket.acc_utilization: GPU compute utilization. Aim for high percentages (e.g., above 80%) to ensure efficient GPU usage.Occasionally, an orange box labeled “No dataset returned for <metric>” may be shown instead of the graph.
This occurs when the ClusterCockpit service was unable to collect the metrics during your job.
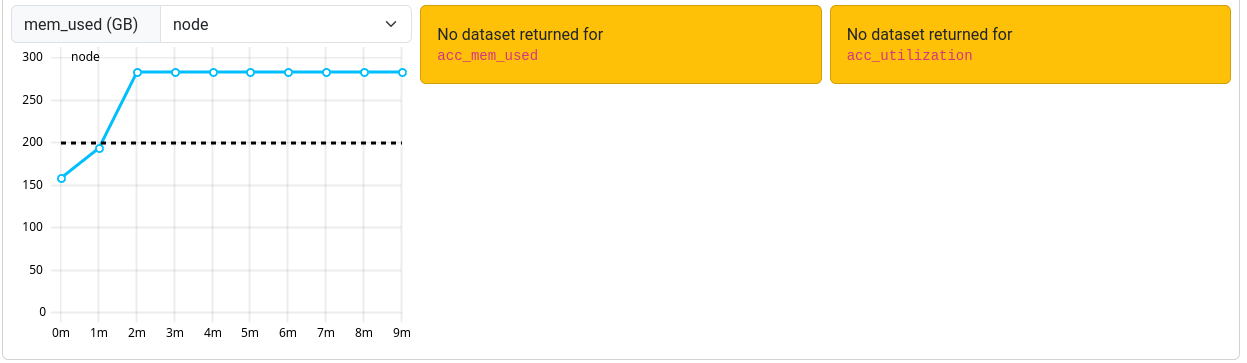
 Note that jobs that ran before March 12th 2025 may report missing or incorrect data in some cases.
Note that jobs that ran before March 12th 2025 may report missing or incorrect data in some cases.
The measurements for ipc and clock are sometimes too high. This is related to power saving features of the CPU. We are currently investigating how to solve this issue.
For jobs that ran before March 7th 2025 a bug triggered an overflow for the power usage metric resulting in unrealisticly high power consumptions.
This bug is fixed, but the fix cannot be applied to older jobs that were affected by it.


Usage of HPC resources differs significantly from handling a regular desktop computer. In order to help people get started we provide two training courses.
In addition to that we recommend online resources. We provide a variety of examples job scripts tailored to Elysium, to get you started with your research.
Linux based operating systems are the de facto standard for HPC systems. Thus it is vital to have a solid understanding of how to work with Linux.
We offer an in-person course that combines a lecture and interactive exercises. The course covers the following topics:
In the trainings we teach participants from wildly different backgrounds, experience, and skill level. Thus, we start with fairly basic topics in the course in order to lay a solid foundation and give everyone a chance to follow along. However, we cannot start at zero. That is why we compiled an interactive Glossary to help you prepare for the course. We expect every participant to be familiar with the listed technical terms and definitions before the training starts.
Dates for the courses are announced via the tier3-hpc mailing list. After the next course date was announced registration can be done via Moodle. We expect all who registered in the course to participate in the next course. Note that the number of participants is limited to 50 people per course. If you change your mind about participation please deregister from the course to free one of the limited spots to others.
If you are already proficient in the topics listed above you may skip the course. It is not a requirement to get access to the cluster. In the Moodle course we provide a quiz where you can check your proficiency with Linux.
Here you may download the slides for the course: Introduction to Linux.
Usage of HPC resources differs significantly from handling a regular desktop computer. Thus it is vital to have a solid understanding of how to work with HPC systems.
We offer an in-person course that combines a lecture and interactive exercises. The course covers the following topics:
In the trainings we teach participants from wildly different backgrounds, experience, and skill level. Thus, we start with fairly basic topics in the course in order to lay a solid foundation and give everyone a chance to follow along. However, we cannot start at zero. That is why we expect every participant to be well acquainted with the topics covered in the Introduction to Linux course as well as a few technical terms and definitions listed in our Glossary before the training starts.
Dates for the courses are announced via the tier3-hpc mailing list. After the next course date was announced registration can be done via Moodle. We expect all who registered in the course to participate in the next course. Note that the number of participants is limited to 50 people per course. If you change your mind about participation please deregister from the course to free one of the limited spots to others.
If you are already proficient in the topics listed above you may skip the course. It is not a requirement to get access to the cluster. In the Moodle course we provide a quiz where you can check your proficiency with HPC systems.
Here you may download the slides for the course: Introduction to HPC.
If you do not want to or cannot participate in the training courses, but still want to learn about Linux and HPC, here we provide a list of a few online resources. Note that those materials might not reflect specifics regarding the hardware or environment of the RUB cluster Elysium.
A SLURM job script usually follows the following steps:
The SLURM HEADER is a section in the script after the shebang.
Every line begins with #SBATCH.
1#SBATCH --nodes=1 # Request 1 Node
2#SBATCH --partition=gpu # Run in partition cpu
3#SBATCH --job-name=minimal_gpu # name of the job in squeue
4#SBATCH --gpus=1 # number of GPUs to reserve
5#SBATCH --time=00:05:00 # estimated runtime (dd-hh:mm:ss)
6#SBATCH --account=myaccount_0000 # Project ID (check with rub-acclist)This way the bash interpreter ignores these lines,
but SLURM can pick them out to parse the contents.
Additionally each line contains one of the
sbatch flags.
On Elysium the flags --partition, --time, and --account are required.
For GPU-jobs the additional --gpus flag needs to be specified and at least 1.
| Flag | Example | Note |
|---|---|---|
--partiton=<partition> |
--partition=cpu |
list of partitions with sinfo |
--time=<dd-hh:mm:ss> |
--time=00-02:30:00 |
maximum time the job will run |
--account=<account> |
--account=snublaew_0001 |
project the used computing time shall be billed to. list of project accounts with rub-acclist |
--gpus=<n> |
--gpus=1 |
number of GPUs. Must be at least 1 for GPU partitions |
| Flag | Example | Note |
|---|---|---|
--job-name=<name> |
--job-name="mysim" |
job name that is shown in squeue for the job |
--exclusive |
--exclusive |
Nodes are not shared with other jobs. |
--output=<filename> |
--output=%x-%j.out |
Filename to contain stdout (%x=job name, %j=job-id) |
--error=<filename> |
--error=%x-%j.err |
Filename to contain stderr (%x=job name, %j=job-id) |
--mail-type=<TYPE> |
--mail-type=ALL |
Notify user by email when certain event types occur. If specified --mail-user needs to be set. |
--mail-user=<rub-mail> |
--mail-user=max.muster@rub.de |
Address to which job notifications of type --mail-type are send. |
If your code reads from some input, or writes output,
the performance can strongly depend on where the data is located.
If the data is in your home, or on the lustre file system
the read/write performance is limited by the bandwidth of the interconnect.
In addition to that a parallel file system has problems
with many small read/write operations by design.
It’s performance shines with reading/writing big chunks.
Thus, it is advisable to create a folder on the local disks in the /tmp/ directory,
and perform all read/write operations in there.
At the beginning of the job any input data is put there in one copy,
and all output data is copied from the /tmp/ directory to its final location in one go.
1# obtain the current location
2HDIR=$(pwd)
3
4# create a temporary working directory on the node
5WDIR=/tmp
6cd ${WDIR}
7
8# copy set of input files to the working directory
9cp ${HDIR}/inputdata/* ${WDIR}
10
11...
12
13# copy the set of output files back to the original folder
14cp outputdata ${HDIR}/outputs/
15
16# tidy up local files
17rm -rf ${WDIR}/*The usable disk space on /tmp/ depends on the node type and resources you allocated. You can find more information to the available storage here.
If your program was build with certain versions of libraries it may be required to provide the same libraries at runtime. Since everybody’s needs regarding library versions is different Elysium utilizes environment modules to manager software versions.
1# unload all previously loaded modules
2module purge
3
4# show all module that are available
5module avail
6
7# load a specific module
8module load the_modules_name_and_version
9
10# list all loaded modules
11module listHow to perform your calculation strongly depends on your specific software and inputs. In general there are four typical ways to run HPC jobs.
Farming jobs are used if the program is not parallelized, or scales in a way that it can only utilize a few CPU cores efficiently. Then multiple instances of the same program are started. Each with a different input, as long as the instances have roughly the same runtime.
1for irun in $(seq 1 ${stride} ${ncores})
2do
3 # The core count needs to start at 0 and goes to ncores-1
4 taskset -c $(bc <<< "${irun-1}") ${myexe} inp.${irun} > out.${irun}
5done
6waitPrograms that incorporate thread spawning (usually via OpenMP) can make use of multiple cores.
1export OMP_NUM_THREADS=${SLURM_TASKS_PER_NODE}
2${myexe} inputIf programs require more resources than can be provided by one node it is necessary to pass information between the processes running on different nodes. This is usually done via the MPI protocol. A program must be specifically programmed to utilize MPI.
1ncorespernode=48
2nnodes=${SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES}
3ncorestotal=$(bc <<< "${ncorespernode}*${nnodes}")
4mpirun -np ${ncorestotal} -ppn ${ncorespernode} ${myexe} inputIn programs that utilize distributed memory parallelization via MPI it is possible to spawn threads within each process to make use of shared memory parallelization.
1nthreadsperproc=2
2ncorespernode=$(bc <<< "48/${nthreadsperproc}")
3nnodes=${SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES}
4ncorestotal=$(bc <<< "${ncorespernode}*${nnodes}")
5export OMP_NUM_THREADS=${nthreadsperproc}
6mpirun -np ${ncorestotal} -ppn ${ncorespernode} ${myexe} inputSupport for offloading tasks to GPUs needs to be incorporated into the program.
1export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
2${myexe} inputThe following example scripts are ready to use on the Elysium cluster.
The only change you need to make is to specify a valid account for the --account flag.
You can use the rub-acclist command to get a list of your available project accounts.
The executed programs do not produce any load and will finish in a few seconds.
The generated output shows where each process/thread ran, and if it had access to a GPU.
Minimal CPU Job Script Example
Shared Memory Job Script Example
Distributed Memory Job Script Example
Hybrid Memory Job Script Example
In the meantime, please see Help.
The following news channels are available:
We offer an open consultation hour every Wednesday 14:00, starting October 1, 2025.
The consultation hour is open to all RUB members - please log in before joining the Zoom meeting.
Zoom link: https://ruhr-uni-bochum.zoom-x.de/j/68445033482?pwd=9o95EZacuJBIQ2F7Nb6ju8U7x4GYjm.1
The HPC User room in the RUB Matrix Server is for exchange and collaboration between HPC users at RUB. Please join!
The HPC team is also present, but please note that you should still contact us at hpc-helpdesk@ruhr-uni-bochum.de if you need a problem solved.
The HPC@RUB cluster Elysium is operated by the HPC team at IT.SERVICES.
Contact us at hpc-helpdesk@ruhr-uni-bochum.de to ask questions or report problems.
Please include as much information as possible to help us identify the problem, e.g. LoginID, JobID, submission script, directory and file names etc., if applicable.
The HPC@RUB team offers two courses:
The HPC Wiki offers information about various HPC topics
The HPC.nrw competence network offers